XML Resource Adapters
The following
documentation is available for XML and Web Service resources:
- Tutorial: Calling a Web Service is a tutorial designed to provide a quick introduction to using XML and Web Service resources. This is recommended as the place to start learning about XML and Web Services resources.
- Working with XML and Web Services Resources provides an overview of the facilities available using XML Resources and Web Service Resources.
- XML Resource Concepts is an in depth technical description of the operation of the XML Resources and Web Service Resources.
- Creating and maintaining XML Resources explains how to use the designer to create and maintain XML Resources and Web Service Resources.
- XML Concepts gives some general information on XML.
This page describes the adapters supplied with the XML resource and parameters to configure them. The web service adapter is described in a separate document
File
Adapter
The file
adapter reads and writes XML documents to files.
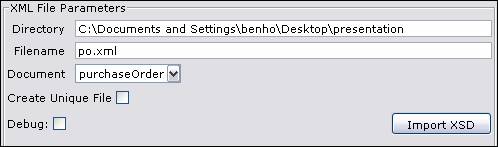
Directory, Filename - Enter the directory and filename of the file to read or write. Directory and Filename both support substitutable parameters. See substitutable parameters section for more details.
Document – Choose one of the resource's documents to read or write.
Create unique filename – When selected, a unique filename
is generated every time the file is written. The unique filename takes
the form filenameNNNN.ext where NNNN is an incrementing
number.
Debug – Flag to debug file adapter
Import XSD – see Importing from an XML schema
A script is
used to read or write a file. The adapter commands are read and write.
Example
To read
from the XML file configured in the myFileAdapter adapter of the MYFILERESOURCE resource.
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
read MYFILERESOURCE 'myFileAdapter'; |
resources.MYFILERESOURCE.read("myFileAdapter"); |
To write to
the XML file.
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
write MYFILERESOURCE 'myFileAdapter'; |
resources.MYFILERESOURCE.write("myFileAdapter"); |
Before a write command, an update command is automatically executed (i.e. non tabular field data
is transferred from the form to the resource).
After a read command, a fetch command is automatically executed (i.e. non tabular field
data is transferred to the form from the resource).
HTTP Adapter
The HTTP
adapter reads or writes XML to an HTTP server.
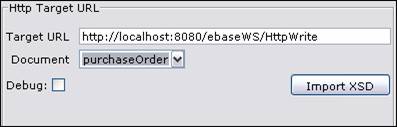
Target URL – Target URL of the HTTP server. Target URL supports substitutable parameters. See substitutable parameters section for more details.
Document – Choose a document to send to the
server (WRITE), or the document receive XML data (READ)
Debug – Flag to debug HTTP adapter
Import XSD – see Importing from an XML schema
A script is
used to send or retrieve XML. The adapter commands are read and write. In a read, the request is an empty GET method. A
response with the XML in the message body is expected.
read – A request with an empty message
body is sent. The message uses the GET method. The message
body of the response is expected to be XML, which is used to populate the
chosen document.
write – The body of the request message
consists of XML from the chosen document. The message uses the POST
method.
Example:
To read XML
from a server as configured in the myHTTPAdapter adapter of the MYHTTPRESOURCE resource.
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
read MYHTTPRESOURCE 'myHTTPAdapter'; |
resources.MYHTTPRESOURCE.read("myHTTPAdapter"); |
To write XML to the same server.
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
write MYHTTPRESOURCE 'myHTTPAdapter'; |
resources.MYHTTPRESOURCE.write("myHTTPAdapter"); |
Before a write command, an update command is automatically executed (i.e. non tabular field
data is transferred from the form to the resource).
After a read command, a fetch command is automatically executed (i.e. non tabular field
data is transferred to the form from the resource).
HTTP
Request/Response Adapter
The HTTP
Request/Response adapter sends XML to an HTTP server in the request message and
retrieves XML from the response message.
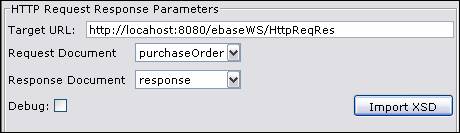
Target URL – Target URL of the HTTP server. Target URL supports substitutable parameters. See substitutable parameters section for more details.
Request Document – Choose a request document. This XML document is sent in the body of the request message. The message uses the POST method
Response Document – Choose a response
document. The body of the response message, which should be valid
XML, is written to this document.
Debug – Flag to debug http request/response
adapter
Import XSD – see Importing from an XML schema
The HTTP
Request/Response adapter is invoked using the call script command.
Example
To call the HTTP server
configured in the myHTTPAdapter
adapter of the MYHTTPRESOURCE resource:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
call MYHTTPRESOURCE 'myHTTPAdapter'; |
resources.MYHTTPRESOURCE.call("myHTTPAdapter"); |
Before a call command, an update command is automatically executed (i.e. non tabular field data
is transferred from the form to the resource).
After a call command, a fetch command is automatically executed (i.e. non tabular field
data is transferred to the form from the resource).
HTTP
Parameter Adapter
The HTTP
Parameter adapter is similar to the HTTP Request/Response adapter. The
difference is that the request document is sent as the value of an HTTP
parameter.
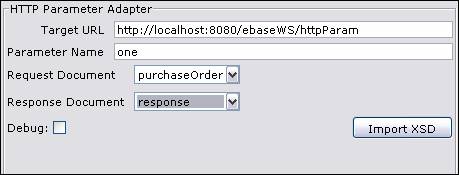
Target URL – Target URL of the HTTP server. Target URL supports substitutable parameters. See substitutable parameters section for more details.
Parameter Name – The name of the HTTP parameter holding the request document.
Request Document – Choose a request document. This XML document will be sent as the value of the parameter. The XML is encoded using standard URL encoding rules (RFC 1738). The message uses the POST method.
Response Document – Choose a response
document. The body of the response message, which should be valid
XML, is written to this document.
Debug – Flag to debug http parameter adapter
Import XSD – see Importing from an XML schema
The HTTP
parameter adapter is invoked using the call
script command. e.g.
Example
To call the HTTP server configured
in the myHTTPParamAdapter
adapter of the MYHTTPPARAMRESOURCE
resource:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
call MYHTTPPARAMRESOURCE
'myHTTPParamAdapter'; |
resources.MYHTTPPARAMRESOURCE.call("myHTTPParamAdapter"); |
Before a call command, an update command is automatically executed (i.e. non tabular field
data is transferred from the form to the resource).
After a call command, a fetch command is automatically executed (i.e. non tabular field
data is transferred to the form from the resource).
Validate
Adapter
This simple
adapter validates the selected document against its XML Schema.
The result of the validation is written to the $COMMAND_STATUS system variable. If the validation is successful, the value will be 'OK', otherwise the value will contain the errors.
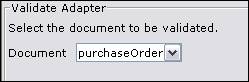
Document – select the document to validate.
The
validate adapter is invoked using the call
script command.
Example
To validate
the document configured in the myInvalidAdatper adapter of the MYRESOURCE resource:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
call MYRESOURCE
'myInvalidAdapter'; |
resources.MYRESOURCE.call("myInvalidAdapter"); |
Log
Adapter
This simple
adapter writes the selected document to the server log.
Document – select the document to log.
The log
adapter is invoked using the call
script command.
Example
To log the
document configured in the myLogAdatper adapter of the MYRESOURCE resource:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
call MYRESOURCE
'myLogAdapter'; |
resources.MYRESOURCE.call("myLogAdapter"); |
XSL Transform
The XSL
adapter provides XSL transform functionality. The source document is transformed
using the provided XSLT text and the result written to the destination
document. As the result must be an XML document, the XSL output method
should be 'xml'.
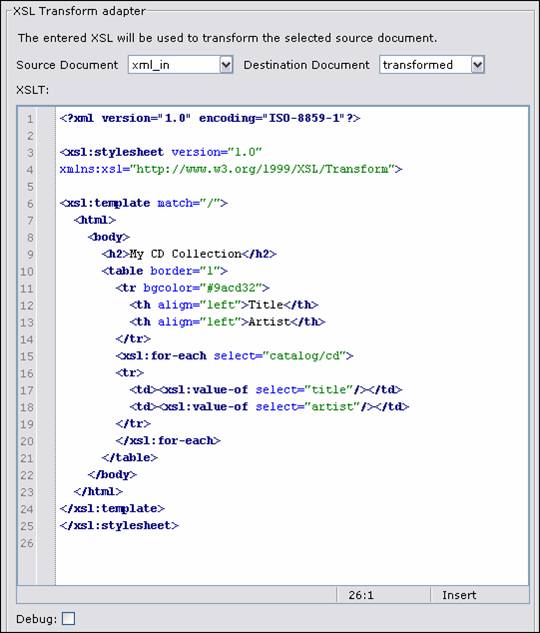
Source document – select the source document for the transform.
Destination document – select the destination document for the transform.
XSLT – Transform text. Type or paste in
a standard XSLT 1.0 document.
Debug – Flag to debug XSL adapter
The XSL
Transform adapter is invoked using the call
script command.
Example
To perform
the transform configured in the myXSLTAdapter adapter of the MYRESOURCE resource:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
call MYRESOURCE
'myXSLTAdapter'; |
resources.MYRESOURCE.call("myXSLTAdapter"); |
Copy
The copy adapter copies XML fragments from one location to
another location. The input and output are both represented by fields in the
resource and are mapped via XPath to document
locations. A deep copy is
performed (i.e. the element and all of its contents). The copy adapter can:
- Serialize XML i.e. copy from a
document to a field
- De-serialize XML i.e. copy from
a field containing an XML string to a document
- Copy a portion of XML from one
document to another
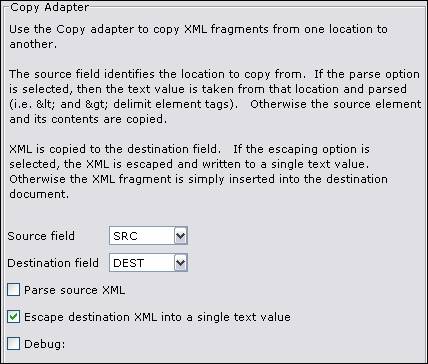
Source field – Identifies the location of the XML to copy.
Destination Field – Identifies where to copy the XML to.
Parse source XML – If this option is selected then the text value of the source field will be used rather than its XML contents. '<' and '&rt;' will be replaced with the XML tag characters '<' and '>' respectively. The text value should represent a valid XML document with a single root element.
Escape destination XML – does the reverse of Parse source XML. The XML is written as the value of the destination
field, escaping XML characters. Normally the value is wrapped in a CDATA
section.
Debug – Flag to debug copy adapter
Click here for examples of using the copy
adapter.
The copy adapter
is invoked using the call script
command.
Example
To perform
the copy configured in the myCopyAdapter of the MYRESOURCE
resource:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
call MYRESOURCE
'myCopyAdapter'; |
resources.MYRESOURCE.call("myCopyAdapter"); |
Stored Procedure
The stored
procedure resource reads XML from and writes XML to a pre-configured database
using a stored procedure call. Note: The stored procedure must be
written and compiled into your database before trying to invoke it from this
adapter. Ebase does not supply this stored procedure but it must be declared
with the following parameters:
|
Parameter Name |
IN/OUT |
Data Type |
|
XML_REQUEST |
IN |
CLOB |
|
XML_RESPONSE |
OUT |
CLOB |
|
ERROR_STATUS |
OUT |
INTEGER |
The name of
the stored procedure is configured within the XML stored procedure resource
adapter panel.
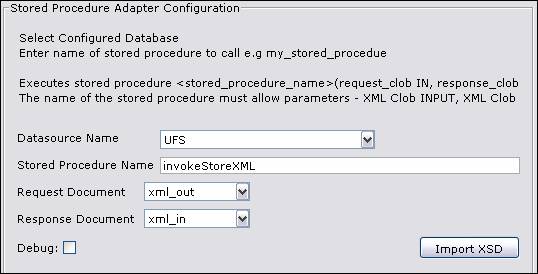
Datasource Name –The Database
Connection from
which the stored procedure is invoked.
Stored Procedure Name – The name of the stored procedure to invoke.
Request
Document – The IN
parameter XML document (request)
Response
Document – The OUT
parameter XML document (response)
Debug – Flag to debug stored procedure
adapter
Import XSD – see Importing from an XML schema
The
ERROR_STATUS OUT parameter is written to the system variable
$COMMAND_STATUS. This is an integer value that can map to the stored procedure
writers own error status codes,
e.g
100 =
SUCCESS
101 =
XML_REQUEST_ ERROR
102 =
XML_RESPONSE_ ERROR
103 =
GENERAL_ERROR
etc…
Example
To invoke
the stored procedure adapter from a script:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
call MYRESOURCE
'myStoredProcedureAdapter'; if [$COMMAND_STATUS != '100'] //error, show error message and display the
command status message E, 1001, $COMMAND_STATUS; endif |
resources.MYRESOURCE.call("myStoredProcedureAdapter"); if (system.variables.$COMMAND_STATUS.value
!= 100) { //error, show error message and display the
command status event.owner.addErrorMessage(1001,
system.variables.$COMMAND_STATUS.value); endif |
JMS Adapter
The JMS (Java Message Server) adapter supports sending and receiving an XML
message to JMS. The JMS adapter supports reading or writing an XML message to
either a JMS queue or JMS topic.
All XML messages are added to or retrieved from JMS as text.
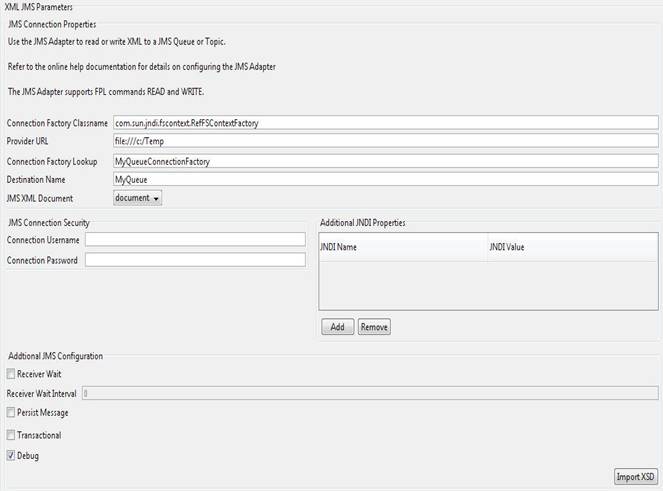
Connection Factory Classname – Identifies the binding connection factory class
name.
Provider URL – The
connection URL of the JMS server.
Connection Factory
Lookup - Identifies Connection Factory JNDI lookup name.
Destination Name –
Identifies the destination object JNDI lookup name.
JMS XML Document – The XML
associated with the read or write.
Connection Username – The
username required to authenticate the JMS connection. This value is optional if
not security is configured on the JMS connection.
Connection Password – The
password required to authenticate the JMS connection. This value is optional if
not security is configured on the JMS connection.
Additional JNDI
Properties – Add values to the JNDI Properties for additional
JNDI lookup parameters required when looking up the connection factory and
destination object.
JNDI Name - java.naming.Context values
required for JNDI Configuration. e.g java.naming.security.principal, this value could be a username for JNDI username
configuration
JNDI Value – The
value associated to the JNDI Name.
Receiver Wait – This is only
applicable when reading from JMS. If selected then a receiver wait interval value is required.
Receiver Wait Interval – This is
only applicable to reading from JMS. This represents the time interval in
seconds to wait for a message to arrive onto the JMS before returning an empty
document. If the value is set to 0 then the receiver will wait indefinitely.
Persist Message – Only
applicable to writing to JMS and flags the document to be persisted by the JMS
for failover and recovery purposes.
Transactional – Flag
whether the message supports transactional behavior on the JMS.
Debug – Flag for
debugging the JMS adapter.
The script commands READ and WRITE are supported by the JMS Adapter. The
system variable $JMS_MESSAGE_ID is set to the message id of the JMS
message when adding or retrieving from the queue or topic.
Example
To invoke from a script:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
write MY_JMS_SEND; set JMS_MESSAGE_ID =
$JMS_MESSAGE_ID; |
resources.MY_JMS.write("SEND"); var msgId = system.variables.$JMS_MESSAGE_ID.value; |
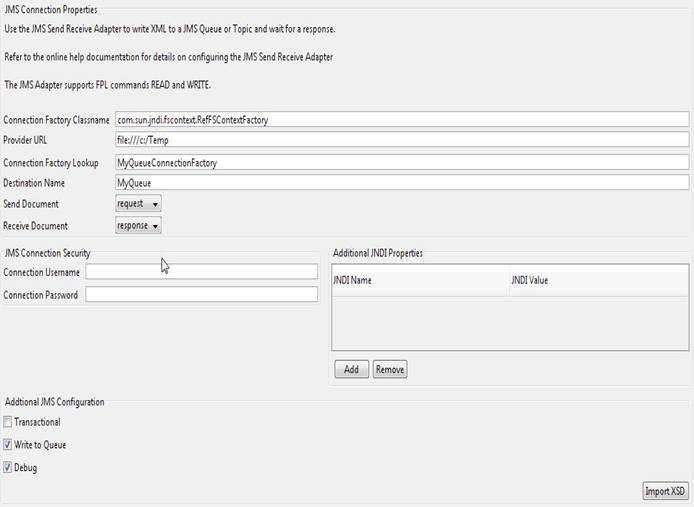
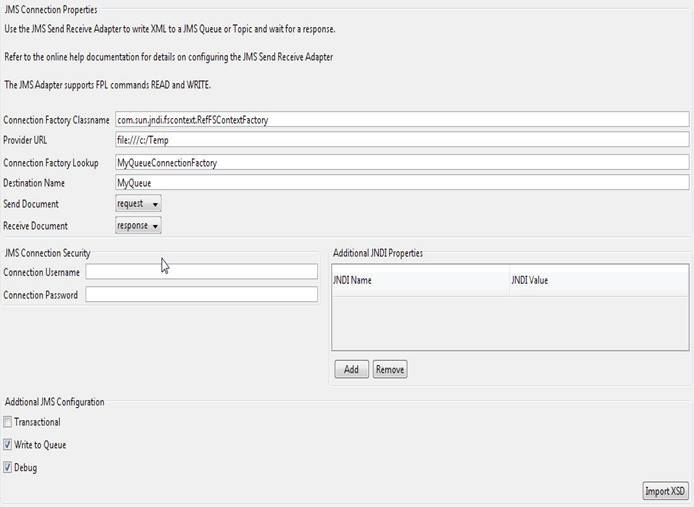
Send Receive JMS Adapter
The Send Receive JMS (Java Message Server) adapter supports a
synchronous sending and receiving an XML message to JMS. The JMS adapter supports
a request/response style message where an XML message is added to a Queue or
Topic and waits until a response document is returned before exiting.
All XML messages are added to or retrieved from the Queue or Topic as text.
Connection Factory Classname – Identifies the binding connection factory
class name.
Provider URL – The
connection URL of the JMS server.
Connection Factory
Lookup - Identifies Connection Factory JNDI lookup name.
Destination Name –
Identifies the destination object JNDI lookup name.
JMS XML Document – The XML
associated with the read or write.
Connection Username – The
username required to authenticate the JMS connection. This value is optional if
not security is configured on the JMS connection.
Connection Password – The
password required to authenticate the JMS connection. This value is optional if
not security is configured on the JMS connection.
Additional JNDI
Properties – Add values to the JNDI Properties for additional
JNDI lookup parameters required when looking up the connection factory and
destination object.
JNDI Name - java.naming.Context values
required for JNDI Configuration. e.g java.naming.security.principal, this value could be a username for JNDI username
configuration
JNDI Value – The
value associated to the JNDI Name.
Transactional – Flag
whether the message supports transactional behavior on the JMS.
Write to Queue – If
selected then the message is written to a JMS queue. If not selected the
message is written to a JMS topic.
Debug – Flag for
debugging the Send Receive JMS adapter.
The script command CALL is supported by the Send Receive JMS Adapter.
The system variable $JMS_MESSAGE_ID is set to the message id of the JMS message when adding or retrieving
from JMS.
The system
variable $JMS_COLLABORATION_ID must be used in conjunction with the Send
Receive JMS Adapter. This variable is set onto the JMS message before writing
to JMS and checks JMS collaboration id is the same when a response is returned
to JMS.
Example
To invoke from a script:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
set $JMS_COLLABORATION_ID = 'MyUniqueID'; call MY_JMS_SEND; set JMS_MESSAGE_ID =
$JMS_MESSAGE_ID; |
system.variables.$JMS_COLLABORATION_ID.value = "MyUniqueID"; resources.MY_JMS.call("SEND"); var msgId = system.variables.$JMS_MESSAGE_ID.value; |
Substitutable Parameters
Some adapters support substitutable parameters that allow you to
substitute parameters values with form field values. The XML resource requires
a source field configured for substitution that is mapped to a field on the
form. These values can be dynamically changed at runtime.
Example
The file adapter Filename and Directory support substitutable field
values.
- Add two
fields to the XML resource, e.g FILENAME and
DIRECTORY
- Import
these fields into the form or map the new fields to existing form fields.
- In a
script:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
set FILENAME = 'customer_details.xml'; set DIRECTORY = 'c:/xmloutput/'; write CUSTOMER_XML; |
fields.FILENAME.value = "customer_details.xml"; fields.DIRECTORY.value = "c:/xmloutput/"; resources.CUSTOMER_XML.write(); |
Use the urlencode
FPL function or method encode() on Java class java.net.URLEncoder when substituting parameters on a URL. If the
target URL for an HTTP XML Adapter is set to
http://localhost:3030/xml?CUSTOMER_NAME=&&CUSTOMER_NAME_ENCODED, the
illegal URL characters will be replaced with as http://localhost:3030/xml?CUSTOMER_NAME=John+Smith.
- Add
field to XML resource, e.g CUSTOMER_NAME_ENCODED
- Import
this field into the form or map the new field to an existing field
- in a
script:
|
FPL: |
API based language
(Javascript): |
|
set CUSTOMER_NAME_ENCODED = urlencode(CUSTOMER_NAME); call MY_HTTP_RESOURCE; |
var custEnc = java.net.URLEncoder.encode(fields.CUSTOMER_NAME.value); fields.CUSTOMER_NAME_ENCODED.value = custEnc; resources.MY_HTTP_RESOURCE.call(); |
See the adapter descriptions for
details of supported substitutable parameters.