Table Basics
What is the
relationship between a table and an external resource?
See also: Tables Tutorial, Tables Tutorial with foreign
keys, Table Control, Repeater Control, Table Display Features, Table Scripting
Introduction
A table represents an array of data values. The data might be loaded from a database, an XML document, or some other external resource, and can also be saved back to the resource. Alternatively, a table might just be used as a temporary working structure in support of the application logic.
A table is
a form-level entity that is created and maintained using the Tables View. This view allows you to create/delete
tables, connect a table to an external resource such as a database, add and
remove columns etc.
A table is
displayed on a page using either a Table Control
or a Repeater Control. A Table Control
displays the table rows in a columnar fashion. A Repeater Control supports a
more flexible display of each repeating table row e.g. each row might be
displayed across multiple lines.
Current row
concept
The system maintains a current row for each table and all
references to column names within a table from script statements are
interpreted as referring to the value of the column on the current row. The
current row is set by the system as follows:
- When
an event is executed for a control inside a table, the current row on the
server is set to the appropriate value; when tables are nested all parent
table values are also set. This applies for controls inside a Table
Control and inside a Repeater Control and for both server-side and
client-side events.
- When
looping through table rows using the FPL loop at table or API TableRowIterator, the current row changes with each successive iteration through the loop. When
all rows have been processed, the current row is reset to its original
value (before the row iteration started). If the row iteration is
interrupted e.g. by an FPL break command, the current row remains
set to the row at the break point.
- Row insertion using the FPL
insertrow FPL command, API Table.insertRow() method or by the user clicking
the add row button all set the current row to the new row.
- Loading
a table using the FPL fetchtable FPL
command or API Table.fetchTable() method sets the first row as the current row.
- Sorting a table using
the FPL sort FPL command or API Table.sort() method sets the first row as the
current row.
- Updating a table using
the FPL updatetable
command command or API Table.updateTable () method may reset the current row in some circumstances.
- A
vertical scroll operation by the user sets the current row to the first
visible row of the new display.
- A
sort operation by the user sets the current row to the first visible row
of the new display.
Note that the current row can also be set directly using the
FPL settablerow() function
or the API Table.setCurrentRow()
method.
Here are some examples of script processing using the
current row concept (see Programming with Tables
for more details):
- A
validation script to check the credit limit column for each row :
API:
if (tables.CUSTOMER.CREDIT_LIMIT.value
> 10000 )
{
event.owner.addErrorMessage("Credit limit exceeds maximum value of 10,000");
}
FPL:
if [CUSTOMER-CREDIT_LIMIT > 10000 ]
message 'Credit limit
exceeds maximum value of 10,000';
endif
The script is specified as a validation event for
table column CUSTOMER-CREDIT_LIMIT. It is executed for each row visible to the
end user. If an error message is issued, it is displayed above the row in error.
- Within
a loop through all table rows:
API:
var orderTotal = 0;
var rows = tables.ORDER_ITEMS.rows();
while (rows.next())
{
if ( tables.ORDER_ITEMS.isRowDeletedByUser() )
{
orderTotal += tables.ORDER_ITEMS.ITEM_AMOUNT.value;
}
}
FPL:
char ORDER_TOTAL = 0;
loop at table ORDER_ITEMS
if [ $ROW_DELETED != 'Y' ]
set ORDER_TOTAL = ORDER_TOTAL +
ORDER_ITEMS-ITEM_AMOUNT;
endif
endloop
- Displaying
a detail page via a hyperlink or a button. In this example the code below
is run as an on click event on column CUSTOMERS-CUSTOMER_NAME of table
CUSTOMERS and column CUSTOMERS-CUSTOMER_NAME has been declared as a
hyperlink. When the user clicks on the link, the current row is set to the
row on which the user has clicked, and details of the selected customer
are then displayed.
API:
form.gotoPage(Pages.CUSTOMER_DETAIL_DISPLAY);
FPL:
goto page CUSTOMER_DETAIL_DISPLAY;
Page CUSTOMER_DETAIL_DISPLAY can
contain any or all of the columns included in the CUSTOMERS table. When this
page is displayed it will contain values from the table's current row i.e. the
row on which the user clicked the link. This list à perform action on selected item is a
common programming construct: the table is loaded with all needed columns, but
only a subset of these (possibly just an id) is initially displayed to the user
as a hyperlink in a table. The user then makes a selection and detailed
processing is performed on that particular item - in this example, the
processing is to display a detail page of the selected item. With Ebase tables,
this type of processing can be achieved with hyperlinks, buttons, or by using
the optional select column
checkbox and then adding one or more buttons at the bottom of the table to
process the user selection(s) and perform specific application functions on
these selections.
What is the relationship between
a table and an external resource?
A table can optionally be 'backed' by an external resource and this backing resource is specified as a property of the table. Data is initially loaded from the external resource by using the FPL fetchtable command or API Table.fetchTable() method. To save data to the external resource, the FPL updatetable command or API Table.updateTable() method is used. Update table processing command takes care of all amendments that have been made to the table including updates, deletions and insertions. For example, the table shown above consists of the following elements:
|
Table: |
CUSTOMER_TABLE |
|
Table Prefix: |
CUSTOMER_TABLE |
|
Backing resource: |
Database
resource CUSTOMERS |
Data is loaded using either:
API:
var rows = tables.CUSTOMER_TABLE.fetchTable();
FPL:
fetchtable CUSTOMER_TABLE;
And saved using either:
API:
tables.CUSTOMER_TABLE.updateTable();
FPL:
updatetable CUSTOMER_TABLE;
Any database resource used with tables must have the For use with table operations radio button checked.
The relationship between a table column and a resource field
is maintained using a field mapping in exactly the same way as for form
fields. These mappings can be displayed and maintained by clicking the mappings
icon on the form toolbar.
It is also possible to include columns in a table which are not backed by an external resource.
Tables with foreign keys
It’s common practice to use foreign keys to link information from other database tables e.g.:
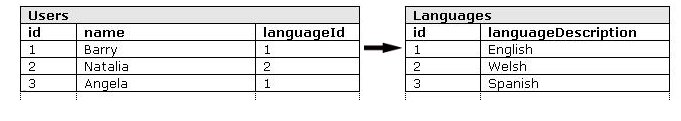
In the above example we have a list of languages identified by a unique number (id) in the Languages table. The Users table has a languageId column which contains a number, this number specifies a language using the unique id of a language in the Languages table. The languageId column is a foreign key.
The requirement is usually to show the table (users in this example) replacing the foreign key (languageId) with a description from the linked table (languageDescription from languages). Additionally, if the table is editable, a dropdown list of languages should be displayed. Ebase Xi supports the display and update of tables in this scenario without the need to write complex SQL to join database tables in the database resource. Click here for a tutorial demonstrating this.
(See Working with
Databases for more information)