Scheduled Tasks
Creating
and Editing a Scheduled Task
Synchronous
and asynchronous execution
Using
the ebasetrigger command
Prerequisites
for using ebasetrigger
Ebase
provided scheduled tasks
Scheduled
Task Logs Maintenance
Writing
a custom scheduled task
See also: Server Administration Application - Scheduled Tasks
Overview
Scheduled Tasks provide the ability to execute programs in background on the server, including the ability to execute forms. This is implemented by three components:
- The Scheduler is an Ebase Xi Server component that is started automatically when the server is started. It wakes up periodically as specified in the server property Scheduler Interval, and then executes any Scheduled Tasks that have a next execution date/time less than or equal to the current date and time. The Scheduler Interval property defaults to 60 seconds. The scheduler supports both single one-off executions and also periodic executions. In addition, execution of a Scheduled Task can also be triggered from an operating system script or from an external system. Each scheduled task execution produces a task log which can be viewed via the Server Administration Application.
- A Scheduled Task is created using the designer and stored in the workspace. It describes the program to run, any input parameters it accepts, and specifies when it should run. The Ebase Xi system is supplied with a number of Scheduled Tasks which provide various routine maintenance functions.
- The Server Administration Application
provides the ability to view scheduled task executions including logs. It
can also be used to execute or suspend a task.
Scheduled Tasks
Creating and Editing a Scheduled Task
A Scheduled Task is created and maintained using the
Scheduled Task editor within the Ebase Xi Designer. A new task is created by
right clicking in the designer tree and selecting New > Scheduled Task.
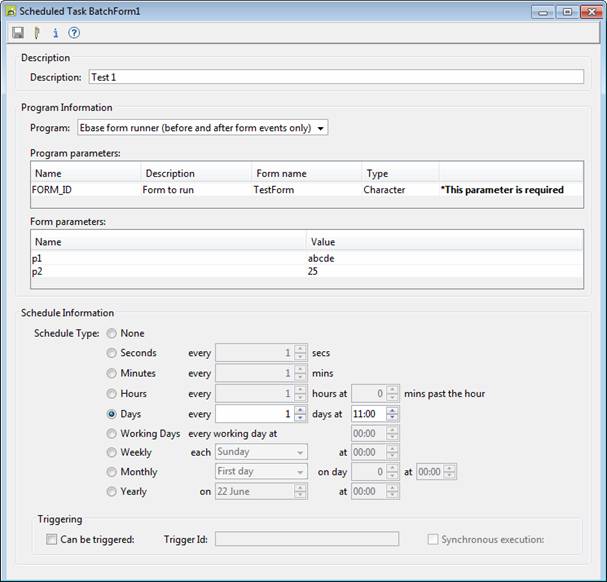
Program information
Program: either select one of the Ebase provided scheduled tasks from the
dropdown list or enter the full Java class name of a custom scheduled task. When a program is entered,
the system will load the specified Java class and present a list of parameters
that the program accepts.
Program parameters: this is a list of all parameters
that can be passed to the selected program. Only the Form name/Value column can be entered and a valid value
should be set according to the Type i.e.
|
Type |
Values |
|
Character |
Any value |
|
Integer |
Any integer value e.g. 1234, 12 |
|
Numeric |
Any numeric value e.g. 1.234 |
|
Boolean |
true or false |
Values for all required parameters must be specified.
Schedule Information
Choose a schedule type from options. If None is selected, the task can only be executed via a trigger or clicking the Run button in the Server Administration Application. If a schedule interval of minutes or seconds is selected, you may need to also adjust the scheduler wake up interval – server property Scheduler Interval. The Working Day Calendar is used by scheduled types that use working days.
Check Can be triggered if the task can be triggered
by an external event. Note that a task can be both scheduled (as
described by schedule type) and triggered. (See triggering task execution)
Trigger id specifies the unique trigger identifier
that is used to trigger execution of the task e.g. MY_TRIGGER. (See triggering task execution)
Synchronous execution indicates that the triggering
system will only receive a response when the task is completed. (See synchronous and asynchronous task
execution)
Triggering task execution
A task can be triggered for execution by either:
- The ebasetrigger
OS command
- Via
URL using an XML interface
In both cases, a trigger id is provided by the caller, and
the scheduled task with the corresponding trigger id is executed.
Synchronous and asynchronous execution
Execution of a triggered task can be either synchronous or
asynchronous. With synchronous execution, the calling process is
notified on completion of the triggered task. With asynchronous
execution, the calling process is notified as soon as the triggered task has
been scheduled for execution.
Verbose mode
When verbose mode is specified, the full execution log of
the triggered task is returned to the caller. This option is only meaningful
when used together with synchronous execution.
Return codes
A return code is always provided from the Java program
called by ebasetrigger. The possible return codes are:
0 Task execution
completed successfully
4 Task execution
completed successfully, but warning messages have been issued. One or more
items may not have been executed
8 Task
execution failed
12 Task execution
not started - system error occurred
16 Task execution not
started – input is invalid
The return code is always returned as a message to the
console e.g.
“Returncode 0 received from Ebase Server.”
In addition, the return code is also returned from the Java
program to the ebasetrigger script.
Using the ebasetrigger command
This consists of both the ebasetrigger.bat (for use
by Windows systems) and ebasetrigger.sh (for use by Linux and Unix
systems) commands and their associated file systems. These commands are
supplied in the External /ebasetrigger directory of the Ebase
product distribution. The entire ebasetrigger directory is
required for execution of the commands and this can be copied to external
systems as required. The ebasetrigger command can be executed from
any system that has network access to the Ebase server.
Prerequisites for using ebasetrigger
ebasetrigger.bat and ebasetrigger.sh are scripts that result
in execution of a Java program, and therefore Java must be installed on the
executing system. If necessary, the full path to the java command can be
specified by editing the script file(s) where the java command can be
found close to the bottom.
Ebasetrigger.properties file
File ebasetrigger.properties in the properties
directory specifies the URL of the trigger servlet on the Ebase server e.g.
serverURL=http://myhost:3030/ufs/ScheduledTaskTrigger
serverURL is a
required property. The host, port and web application parts of the URL should
be changed to match the location of the Ebase Xi Server. The servlet name – ScheduledTaskTrigger – should not normally be changed.
In addition, the following optional properties can be specified. These act as
defaults for all ebasetrigger commands that use the properties file
unless the corresponding parameter is specified as part of the ebasetrigger
command.
ExecutionMode: can have values sync
or async
Verbose: can have values true and false
User: userid specified in the Ebase Xi security system
Password: password
ebasetrigger command syntax
The syntax is as follows:
ebasetrigger
[-help] –user userid –password pwd [-sync/-async] [-verbose]
triggerid [P1=value1] [P2=value2 ....]
where…
user userid specifies
the userid in the Ebase Xi security system(required
unless user is specified in the ebasetrigger.properties file)
password pwd specifies
the password (required unless password is specified in the ebasetrigger.properties
file)
help shows
usage syntax (optional)
sync indicates
execution is synchronous (optional)
async indicates
execution is asynchronous (optional)
verbose all
messages will be issued to the caller (optional)
triggerid trigger
id (required)
Pn=valuen any
number of name/value parameter pairs to be passed to the Ebase triggered task
(optional)
examples:
ebasetrigger
ABCD
ebasetrigger –user fred –password bloggs –sync ABCD
ebasetrigger
–user fred –password bloggs –sync –verbose ABCD
ebasetrigger
–sync –verbose ABCD PNAME=Fred OPTION1=true OPTION2=false
where ABCD is the trigger id, and PNAME, OPTION1 and OPTION2
are parameters accepted by the triggered task.
Using the XML interface
The XML interface is provided as part of the Ebase Server by
the ScheduledTaskTrigger servlet, which accepts an EbaseTriggerRequest
document and responds with an EbaseTriggerResponse document.
The EbaseTriggerRequest document is illustrated
below:
<EbaseTriggerRequest
user=”fred” password=”bloggs”>
<TriggerId>ABCD</TriggerId>
<Synchronous>true</Synchronous>
<Verbose>true</Verbose>
<Parameters>
<Parameter>
<ParameterName>PNAME</ParameterName>
<ParameterValue>Fred</ParameterValue>
</Parameter>
<Parameter>
<ParameterName>OPTION1</ParameterName>
<ParameterValue>true</ParameterValue>
</Parameter>
<Parameter>
<ParameterName>OPTION2</ParameterName>
<ParameterValue>false</ParameterValue>
</Parameter>
</Parameters>
</EbaseTriggerRequest>
where the <Synchronous>, <Verbose> and <Parameters> tags are optional. The minimum requirement is as follows:
<EbaseTriggerRequest
user=”fred” password=”bloggs”>
<TriggerId>ABCD</TriggerId>
</EbaseTriggerRequest>
The system
will respond with an EbaseTriggerResponse document which is
illustrated below:
<EbaseTriggerResponse>
<TriggerId>ABCD</TriggerId>
<ReturnCode>0</ReturnCode>
<ExecutionLog>Execution
completed with return code 0</ExecutionLog>
</EbaseTriggerResponse>
If the task is executed with the verbose and synchronous options, the <ExecutionLog> element will contain the complete execution log for the task.
Logging of triggered tasks
All task logs for triggered tasks are saved in the same way
as for scheduled tasks, and these can be viewed online using the Server Administration Application.
Ebase provided scheduled tasks
The following Ebase scheduled tasks are provided and can be
selected from the program dropdown list of available programs:
Batch Execution
This program executes batches in background. It accepts the
following parameters:
|
Name |
Description |
|
BATCH_NAME |
Name of batch to execute. * can be used as a mask character e.g. A* indicates all batches beginning with A. * alone indicates all batches. |
|
INCLUDE_ERRORS |
Enter 'true' or 'false' to indicate whether or not the
program should re-execute batches with status Error. |
(See Ebase Xi Batch System
for more information)
Batch Maintenance
This program deletes batches with status 'OK' from the
database. (See Ebase Xi Batch System for more
information)
|
Name |
Description |
|
NO_DAYS |
Number of days to keep batches before deletion |
Snapshots Maintenance
This program deletes expired snapshots from the database. Snapshots are created by the Snapshot Manager. This program accepts no parameters.
Saved Forms Maintenance
This program deletes expired saved forms from the database.
Saved forms are created by end users using the save/restore feature. This
program accepts no parameters. (See Save/Restore
Feature for more information)
Scheduled Task Logs Maintenance
This program deletes scheduled task logs from the database
after the specified number of days.
|
Name |
Description |
|
NO_DAYS |
Number of days to keep task logs before deletion |
Form Runner
This program executes the specified form, running the
before-form and after-form events. All other events are ignored.
|
Name |
Description |
|
FORM_ID |
The name of the form to run |
When a form has been selected, an additional table of form parameters is displayed which contains all form fields marked as URL Parameters. This makes it possible to pass parameter values into forms executed by the scheduler.
Deployments Maintenance
This program deletes deployments from a server system which
have not been actioned for the specified number of days.
|
Name |
Description |
|
NO_DAYS |
Number of days since the deployment was last actioned before deletion |
Workflow Maintenance
This program can be used to either delete or archive
completed jobs from the workflow runtime database. Archiving removes completed jobs
from the runtime database and copies them to the archive database. The archive
database tables have the same name as the corresponding runtime tables but
ending with “_archive”.
|
Name |
Description |
|
NO_DAYS |
Number of days to keep completed workflow before deletion |
|
ARCHIVE |
When 'true' completed jobs are archived When ‘false’ completed jobs are deleted |
Writing a custom scheduled task
Custom scheduled tasks can be scheduled for execution by the
Scheduler in the same way as Ebase supplied scheduled tasks. Each scheduled
task runs a custom written Java program that must conform to the following
specification:
- Must
extend com.ebasetech.ufs.batch.ExecutableTask
- Must
have a single public execute() method. The parameter types must be
one of the following types: String, Integer, Float, BigDecimal, Boolean.
These parameters will then be displayed in the scheduler dialog above.
- Must
provide a getParameters() method (see example below).
- Must
return with an integer to indicate execution status (constants are
provided)
- The
class file must be on the classpath of the Ebase Server.
The program can log messages by using the log(messageString)
method. Start and end messages are automatically created and do not need to be
added.
To terminate abnormally, the program can throw a ScheduledTaskAbortException.
The class will need to include the following import
statement:
import com.ebasetech.ufs.batch.*;
and have the ufs.jar file on the compile classpath.
This jar file is located in .../ufs/UfsServer/tomcat/webapps/ufs/WEB-INF/lib.
To make the program available to the Ebase Server either:
- Add
the custom task jar file to
.../ufs/UfsServer/tomcat/webapps/ufs/WEB-INF/lib
- Add the
.class file to .../ufs/UfsServer/tomcat/webapps/ufs/WEB-INF/classes
Example:
import com.ebasetech.ufs.batch.*;
public class ScheduledTaskLogsMaintenance extends ExecutableTask
{
private static final String
PARAMETER_NO_DAYS = "NO_DAYS";
private static final String
PARAMETER_NO_DAYS_DESCRIPTION = "Number of days";
private static final int
DEFAULT_NO_DAYS = 30;
public int execute( ) throws
ScheduledTaskAbortException
{
/* Get Parameters */
int noDays;
Integer noDaysInt =
(Integer)getParameterValue( PARAMETER_NO_DAYS );
if ( noDaysInt == null )
{
noDays =
DEFAULT_NO_DAYS;
}
else
{
noDays =
noDaysInt.intValue();
}
log( "Deleting scheduled
task logs older than " +
beforeDate.substring( 6 ) +
SystemDate.DATE_DELIMITER +
beforeDate.substring( 4, 6 ) +
SystemDate.DATE_DELIMITER +
beforeDate.substring( 0, 4 ) );
/* Now perform the task function
*/
deleteLogs( beforeDate );
return STATUS_OK;
}
public List getParameters( )
{
ArrayList list = new
ArrayList(1);
ScheduledTaskParameter parm = new
ScheduledTaskParameter(
PARAMETER_NO_DAYS,
ExecutableTask.PARAMETER_TYPE_INTEGER, PARAMETER_NO_DAYS_DESCRIPTION );
list.add( parm );
return list;
}
}