Publishing RESTful Web Service Documentation
Publishing RESTful Web Service
Documentation
See also:
Publishing RESTful Web Service Documentation
Ebase publishes RESTful Web Service using the Swagger framework to generate JSON or YAML documents. Swagger is a framework that generates a simple representation of the RESTful service API. Swagger provides descriptive documentation about your REST API. Swagger UI tools also provide an interactive test framework to the REST API.
To generate either JSON or YAML documents:
Swagger JSON URI
http://<domain-name>:<port>/<web-app>/api/<service_name>/swagger.json
Swagger YAML URI
http://<domain-name>:<port>/<web-app>/api/<service_name>/swagger.yaml
It is possible to
copy and paste either the JSON or YAML documents or load the URL above into any
Swagger reader to view the documentation and interactively test the API.
Swagger tools make it possible to create many client API’s, e.g
JavaScript or Java. Click here for more information about generating client interface framework.
The Ebase server
contains an integrated Swagger UI to view and test the published Swagger
documentation. The JSON document is converted to a web page that displays the
documentation about the RESTful Web Service and the
associated endpoints. The documentation can be accessed through the designer by
clicking the ![]() icon in the RESTful
Web Service toolbar or directly by entering the URL into a browser.
icon in the RESTful
Web Service toolbar or directly by entering the URL into a browser.
The external URL to
view the published documentation is as follows:
http://<domain-name>:<port>/<web-app>/ebasePublishRest.eb?serviceName=<service-name>
See View Published Documentation for more
information.
Editing
Swagger Documentation
Open the RESTful Web Service
that you would like to edit the documentation. Click on the ![]() icon in the toolbar to open the sub menu then
click on the
icon in the toolbar to open the sub menu then
click on the ![]() located on the dropdown to open the
documentation dialog.
located on the dropdown to open the
documentation dialog.
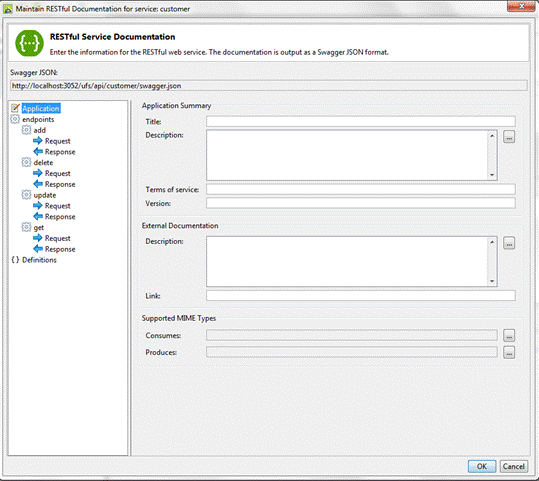
The left
hand panel displays a tree structure for editing various sections of the
documentation. Click on the appropriate node to show documentation fields in
the right hand panel for:
Application: Overview of the RESTful
Web Service.
Endpoints: This contains list of endpoints contained
within the RESTful Web Service.
Request: Documentation related to the incoming
request
Response:
Documentation related to the outgoing response.
Definitions: List of structures to create individual
object types or full JSON/XML structures.
Application
The
application panel documents the overview of the RESTful
Web Service and consists of the following fields:
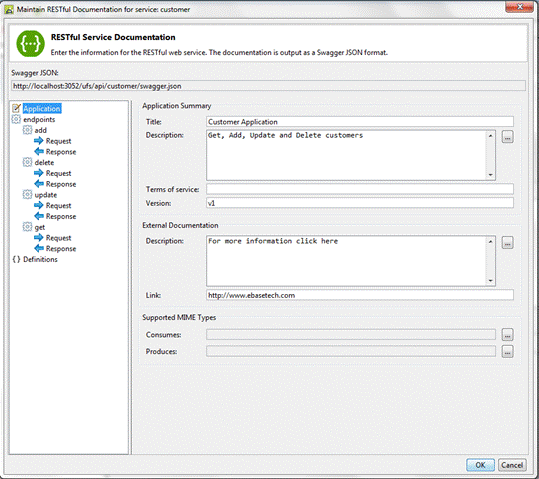
Title: This is required
and contains the title of the application.
Description: A short description of the RESTful
Web Service. HTML and GFM syntax can be used for rich
text representation
Terms of service: The Terms of Service for the API.
Version: This is required
and provides the version of the application API.
External Documentation: Additional external documentation
for this application.
Description: A short description of the target
documentation. HTML and GFM syntax can be used for rich
text representation.
Link: Link to an external website
Supported Mime Types:
Consumes: List of
the MIME types that
the RESTful Web Service accepts. This is global to all endpoints but
can be overridden on specific endpoints.
Produces: List of
the MIME types that
the RESTful Web Service returns. This is global to all endpoints but
can be overridden on specific endpoints.
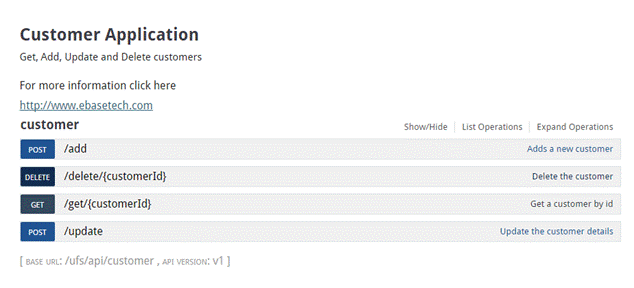
The figure
below shows the Application information when viewed in the external browser.
Click the ![]() icon to view the documentation to view the
published documentation.
icon to view the documentation to view the
published documentation.
Endpoints
Click on
the endpoint name to edit the documentation for the specific endpoint.
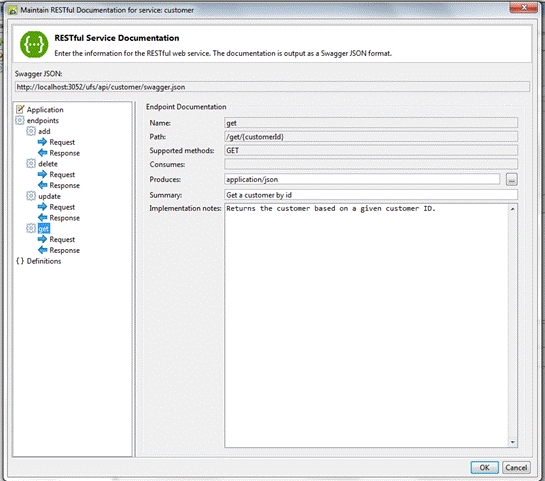
Name: Read only field that displays the name of the
endpoint.
Path: Read only field that displays the path for the
endpoint URI.
Supported Methods: Read only field that displays the HTTP methods
for the endpoint.
Consumes: List of the MIME types that the
endpoint accepts.
This value overrides the global consumes property.
Produces: List of the MIME types that the
endpoint returns.
This value overrides the global produces property.
Summary: A short summary of the endpoint functionality.
For maximum readability in the swagger-ui this field
SHOULD be less than 120 characters.
Implementation Notes: A verbose explanation of the endpoint functionality. HTML and GFM syntax can be used for rich
text representation.
Request Documentation
Click on
the ![]() Request node to edit the documentation for the
incoming request.
Request node to edit the documentation for the
incoming request.
Path
Parameters
The path
parameters table is automatically populated with the path parameters that are
in the endpoint URI. Path
parameters are enclosed within {}, e.g /customer/{customerId}.
It is not
possible to add additional parameters to the path parameters table.
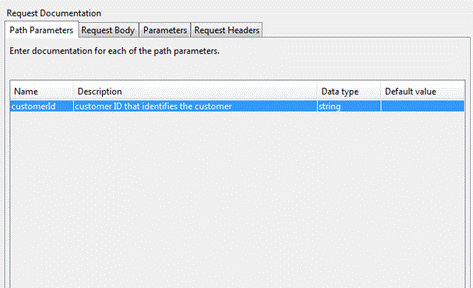
Name: This is a read only column and is the name of
the parameter extracted from the endpoint
URI.
Description: A short description about the parameter. This
could contain examples of use. GFM syntax can
be used for rich text representation.
Data Type: This is required. The value
MUST be one of "string", "number", "integer", "boolean". The default data type is a string.
Default Value: Specify a default value to populate the
parameters field in the documentation.
Request Body
Add
documentation for the request body. The request body is only applicable for
HTTP POST and PUT requests.
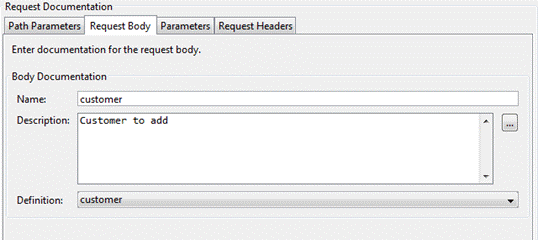
Name: Enter a one word description of the request
type.
Description: short
description about the parameter. This could contain examples of use. GFM syntax can
be used for rich text representation.
Definition: Select the definition
reference for the request body.
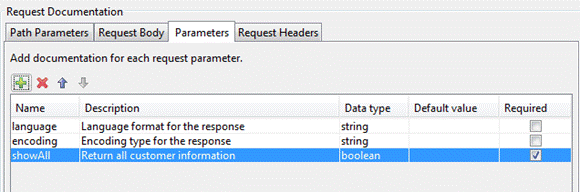
Parameters
The
parameters table contains a list of the Query or Post parameters for the
request. Parameters are not configurable from the RESTful
Web Service Editor but should be added to the documentation if they are
required at runtime.
Click the ![]() icon to add a new parameter.
icon to add a new parameter.
Click the ![]() icon to delete the selected parameter.
icon to delete the selected parameter.
Click the ![]() icon to move the parameter up the list.
icon to move the parameter up the list.
Click the ![]() icon to move the parameter down the list.
icon to move the parameter down the list.
Name: This is required.
Enter a name for the parameter.
Description: A short description about the parameter. This
could contain examples of use. GFM syntax can
be used for rich text representation.
Data Type: This is required. The value
MUST be one of "string", "number", "integer", "boolean". The default data type is a string.
Default Value: Specify a default value to populate the
parameters field in the documentation.
Required: When selected this prompts the user that the
field must be entered.
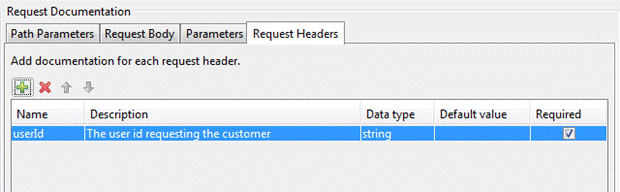
Request
Headers
The headers
table contains a list of the HTTP headers for the request. Request headers are
not configurable from the RESTful Web Service Editor
but should be added to the documentation if they are required at runtime.
Click the ![]() icon to add a new request header.
icon to add a new request header.
Click the ![]() icon to delete the selected request header.
icon to delete the selected request header.
Click the ![]() icon to move the request header up the list.
icon to move the request header up the list.
Click the ![]() icon to move the request header down the list.
icon to move the request header down the list.
Name: This is required.
Enter a name for the request header.
Description: A short description about the request header.
This could contain examples of use. GFM syntax can
be used for rich text representation.
Data Type: This is required. The value
MUST be one of "string", "number", "integer", "boolean". The default data type is a string.
Default Value: Specify a default value to populate the request
headers field in the documentation.
Required: When selected this prompts the user that the
field must be entered.
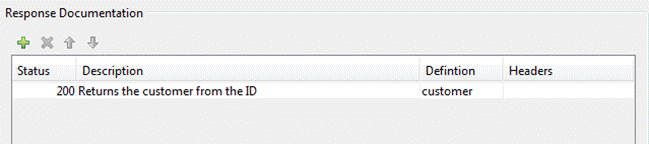
Response Documentation
Click on
the ![]() Response node to edit the documentation for
the outgoing response.
Response node to edit the documentation for
the outgoing response.
Click the ![]() icon to add a new response.
icon to add a new response.
Click the ![]() icon to delete the selected response.
icon to delete the selected response.
Click the ![]() icon to move the response up the list.
icon to move the response up the list.
Click the ![]() icon to move the response down the list.
icon to move the response down the list.
Double
click a response to edit the response documentation.
When adding
or editing a HTTP response a dialog is opened with two tabs:
Response Information
Enter the
documentation for the response.
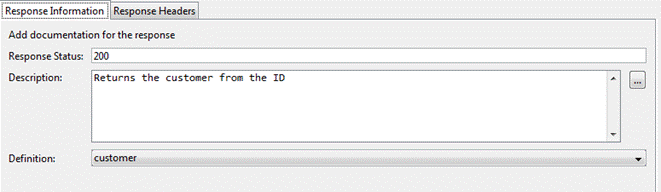
Response Status: Enter the response status code for the
response. If no status is entered the response is displayed as a default response. This indicates that
this is the default response for all statuses; this excludes the others
responses specified.
Description: Enter a description about the response. This
could contain examples of use. GFM syntax can
be used for rich text representation.
Definition: Select the definition
reference for the response body. Response bodies are only applicable to HTTP
GET, POST and PUT responses.
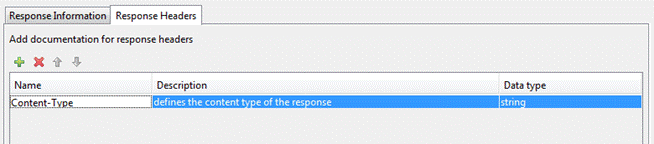
Response Headers
Enter the
documentation for the response headers.
Click the ![]() icon to add a new response header.
icon to add a new response header.
Click the ![]() icon to delete the selected response header.
icon to delete the selected response header.
Click the ![]() icon to move the response header up the list.
icon to move the response header up the list.
Click the ![]() icon to move the response header down the
list.
icon to move the response header down the
list.
Name: This is required.
Enter a name for the response header.
Description: A short description about the response header.
This could contain examples of use. GFM syntax can
be used for rich text representation.
Data type: The value can be one of "string", "number", "integer", "boolean". The default data type is a string.
Definitions
A definition contains a
tree structure containing data nodes. A definition is used to organize and
structure objects that define a structure that represents a JSON or XML
structure. JSON structures can have multiple data nodes at the root of the
definition node where as XML structures can only contain one root node.
The definitions are used when defining the incoming Request Body
and the outgoing Response Body of the RESTful
Web Service. A data node where its type is set to ‘object’ can reference
another definition.
Click on the ![]() icon to show the definitions. This opens the Definitions View Panel. The Definitions View Panel shows a list of
the definitions in a tree. To the right of the tree is the Data Node Properties panel to edit the individual data nodes.
icon to show the definitions. This opens the Definitions View Panel. The Definitions View Panel shows a list of
the definitions in a tree. To the right of the tree is the Data Node Properties panel to edit the individual data nodes.
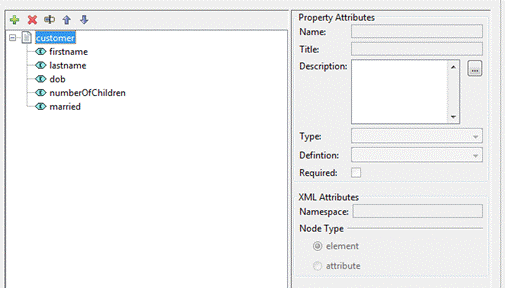
The three icons used in the Definitions View are:
![]() - A single Definition structure.
- A single Definition structure.
![]() - indicates a basic type, JSON object or an
XML element
- indicates a basic type, JSON object or an
XML element
![]() - indicates and XML attribute and is only used
for XML only structures.
- indicates and XML attribute and is only used
for XML only structures.
Definition
To add a new definition - Click the add toolbar icon ![]() and select
and select ![]() Add
definition from the drop down menu.
Add
definition from the drop down menu.
To rename a definition - Select the definition and click the rename toolbar icon ![]() .
Enter a new name in the definition name dialog box.
.
Enter a new name in the definition name dialog box.
To delete a definition - Select the definition and click the delete toolbar icon ![]() .
.
Data nodes
To add a new data node - Select the parent Data node of the new
node. Click the add toolbar icon ![]() and select
and select ![]() Add node
from the drop down menu. The new node
will be selected and its properties can be edited in the data node properties
panel.
Add node
from the drop down menu. The new node
will be selected and its properties can be edited in the data node properties
panel.
To delete an data node - Select the node and click the delete toolbar icon ![]() . This node, all of its sub structure and
attached fields will be deleted.
. This node, all of its sub structure and
attached fields will be deleted.
To rearrange sibling nodes – Use the move down ![]() and move up
and move up ![]() buttons to change the order of adjacent XML
nodes. XML Attributes will always appear
before elements.
buttons to change the order of adjacent XML
nodes. XML Attributes will always appear
before elements.
The location of data nodes can also be changed using drag and drop
functionality.
Data Node properties
panel
The Data Node Properties panel shows the
properties of the selected Data node.
All properties are editable.
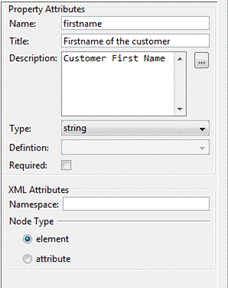
Name – data node name of the selected node.
Title
– Short
description of the data node
Description - A short
description about the data node. This could contain examples of use. GFM syntax can
be used for rich text representation.
Type - The drop down lists some or the common
data types. By selecting ‘object’ in the
type field enables the Definition
field below.
Definition - Select the definition for the ‘object’ type.
Required
– By
checking the required checkbox indicates that the value must be entered.
XML Attributes – The following attributes are specific to
XML structures only.
Namespace – The namespace for the XML element
Node
Type - Select either
element or attribute.
Data Node Data Types
The data nodes type can be set to either: array, boolean, decimal, double, float, integer, long, object or string. If a data node type is set to <none> then the node can contain children to create a tree structure used in JSON and XML structures.
If the data node is set to ‘array’ then the node can contain one child and this child must have a data type set.
View Published Documentation
Open the RESTful Web Service
and click on the ![]() icon in the toolbar to open the sub menu then
click on the
icon in the toolbar to open the sub menu then
click on the ![]() icon to view the documentation to view the
published documentation. This will launch an external browser window. The RESTful Web Service must be saved if modified to view any
documentation changes.
icon to view the documentation to view the
published documentation. This will launch an external browser window. The RESTful Web Service must be saved if modified to view any
documentation changes.
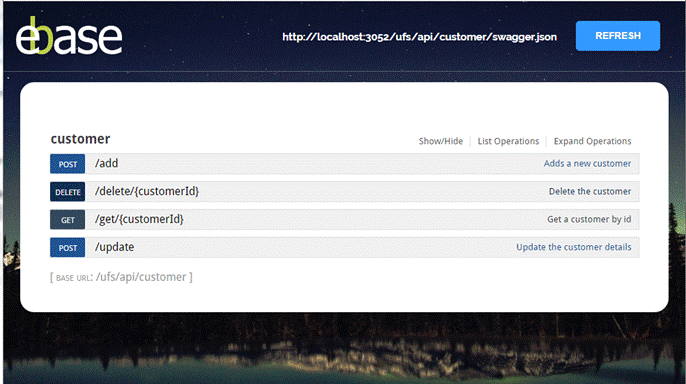
The URL to the
published documentation is formatted as:
http://<domain-name>:<port>/<web-app>/ebasePublishRest.eb?serviceName=<service-name>
The figure below
shows the published documentation:
Viewing and Testing Endpoints
Click the endpoint name
to expand the information on the endpoint. To test the endpoint - enter
information into the appropriate fields and click the ![]() button.
button.
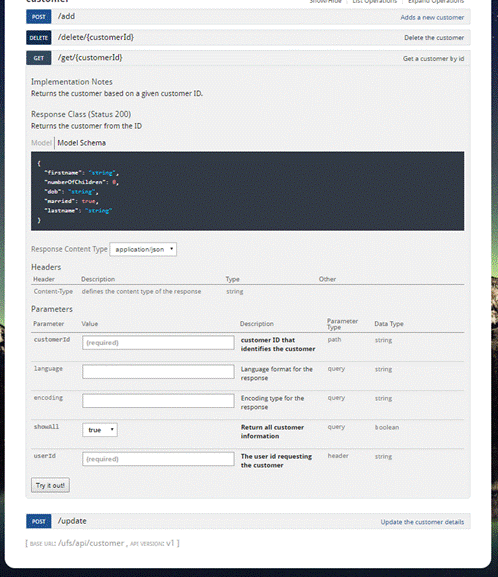
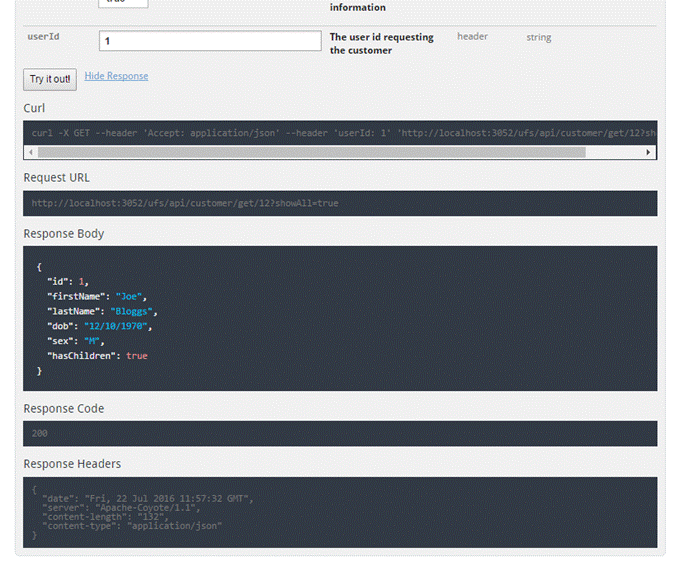
The figure below
shows an endpoint configured as a HTTP GET and returns a customer from a
supplied customer id path parameter.
The figure
below shows the response after filling in the form from the figure above and
clicking the ![]() button.
button.
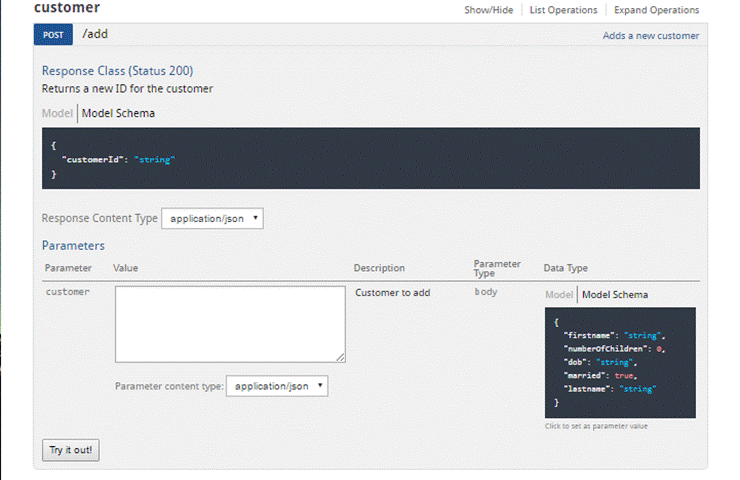
The figure below
shows an endpoint configured as a HTTP POST that accepts a customer JSON object
and returns a newly create customer id.